Table of Contents
Toggle
A broken bone, sprain, or strain are very common but painful injuries that can affect a person of any age. Since these injuries happen all the time and can happen to anyone around you, whether at home or outside, therefore it is important to know the right first aid techniques to limit the effects of the conditions and ease pain. However, knowing whether a person has a broken bone or just a soft tissue injury is tricky. So, let’s learn the signs and symptoms of a fractured bone, sprain, and strain and find out how you should give first aid to the patient.
Importance of First Aid in Treating Fractures, Sprains, and Strains
These musculoskeletal injuries are not life-threatening, but they require immediate medical care to prevent further injury and deterioration of the condition. Moving injured limbs may increase pain and bleeding and could lead to tissue damage; however, timely first-aid can prevent the original injury from severing. Therefore, immediate first aid is crucial for fractured bones, sprains, and strains.
What are fractures?
A fracture is a broken bone or cartilage. The break or a crack can be partial or complete. It occurs when the force exerted against the bone is stronger than a bone can withstand.
Causes of Fractures
Fractures can occur for many reasons, such as:
- Accidents: They often happen due to an accident, sports injury, trauma, or due to a direct blow or kick to the body.
- Overuse: Fractures can also be caused due to overuse or repetitive motion that tires muscles and put more pressure on the bone.
- Osteoporosis: Another reason for fractures is diseases like osteoporosis or bone cancer. Osteoporosis weakens the bones and makes them more susceptible to breaks and fractures. The most common fractures in osteoporosis patients are that of the hips, vertebrae, wrist, and arms. These fractures are very painful and debilitating.
Classification of Fractures
Fractures can be classified into two categories:
- Open Fractures- These kinds of fractures are also known as compound fractures. In it, either a deep wound exposes the bone through the skin, or the bone comes out of the skin and can be seen.
- Closed Fractures- These types of fractures are also known as simple fractures. The bone breaks partially or completely, but the skin remains intact.
Different Types of Fractures
| Type of Fracture | Definition |
| 1. Hairline Fracture | It is a very thin crack or break in the bone. It usually occurs in the foot or lower leg due to repeated stress from running or jogging. |
| 2. Stress Fracture | These fractures are caused by repetitive stress to a bone. Repetitive motions like running cause stress fractures. These fractures are difficult to diagnose with regular X-rays. |
| 3. Complete Fracture | It occurs when a bone breaks into two pieces and separates from each other completely. The cortex completely separates circumferentially. |
| 4. Greenstick Fracture | It is a small, slender crack in the bone, or in other words, when the bone cracks on one side only and not all way through. It occurs in children as their bones are more flexible than that of adults. |
| 5. Comminuted Fracture | This fracture occurs when the bone is broken into more than two pieces or crushed into small pieces. These tend to heal more slowly. |
| 6. Spiral Fracture | These are also called torsion fractures and occur when a rotating force or torque is applied to the bone along its axis. In it, at least one part of the bone twists during a break. |
| 7. Depression Fracture | It is the fracture, especially of the skull, where the cranial bone breaks, and the depression of the bone is in towards the brain. In simple words, it occurs when the skull is fractured inwards. |
| 8. Complicated Fracture | It is a fracture where broken bone damages vital organs. For example, lungs can be punctured due to fractured ribs. There may be damage to veins, arteries, nerves, or the lining of the bone. |
| 9. Transverse Fracture | In this fracture, the bone breaks in a straight line across the bone. It occurs when a strong impact takes place perpendicularly to the bone’s axis. Traumatic events like falls or automobile accidents can cause it. |
| 10. Oblique Fracture | It happens when the bone breaks diagonally or at a steep angle. Most often, it occurs in long bones. |
What are Sprains, Strains, and Dislocations?
Sprains
A sprain is an injury when the ligaments or fibrous tissue that connect bones at a joint either pull or tear. In the first-degree sprain, the ligament is stretched; in the second-degree sprain, the ligament is partially torn; in a third-degree sprain, the ligament is completely torn. The most common areas a sprain occurs are the fingers, wrist, ankle, and knee.
Strains
Strains are overstretched or torn muscles (also known as pulled muscles). It involves an injury to muscles or tendons. It can be caused by stretching, pulling, or twisting of the muscle or tendon. It is most common in the knees, feet, legs, and back.
Dislocations
Dislocations are an injury where the bones of the joint slip out of their normal positions. A joint can be partially or fully dislocated. It usually involves the larger joints of the body. They can be extremely painful and cause the affected joint area to be immobile or unsteady. It can be caused by a trauma usually resulting from a fall, accident, or collision during contact or high-speed sports. Although it can happen to any joint, most often, dislocation affects the joints of the finger, shoulder, knee, hip, jaw, or elbow.
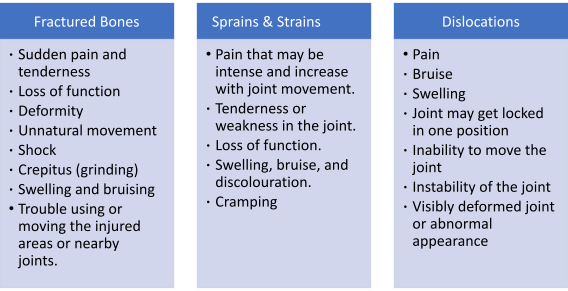
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Fractured Bones, Sprains & Strains, and Dislocations
A person may have the following signs and symptoms in each case:
What Are the General Treatment Principles?
The general treatment practices you should adopt in case of a fracture, sprain, strain, or dislocation are as follows:
- Stop the activity
- Survey the injured area
- First Aid, if qualified
- Get help in case you are not qualified
- Determine if additional medical attention is required
How Can a Paramedic Help?
A fracture, sprain, strain, and dislocation can happen easily. However, when an injury occurs, there can be bruising, swelling, and damage, and if first aid is not given properly and timely, it may cause further damage to the body part. The paramedics can use the following techniques to limit swelling and damage.
RICE
The RICE first aid method can be given for up to 72 hours after a strain, sprain, or fracture. It limits swelling and speeds up recovery.
- Rest- After an injury, stop the person from moving the injured limb, as any movement can increase bleeding and swelling. So, rest the patient and the injured body part.
- Ice- Use ice packs wrapped in light cloth for 15-20 minutes every 2-4 hours for 48 to 72 hours.
- Compression- Apply a compression bandage firmly to extend well around, above, and below the injury. Overlap each layer by half. If you think it is a fracture, ensure the patient cannot move the limb. You must ensure the bandage is not too tight.
- Elevation- Elevate the injured area to reduce swelling. If a patient has significant loss of function or severe pain, then ensure the patient sees a doctor immediately.
Splinting
It is the most common procedure for immobilizing the injured body part and preventing further damage. You can use this technique to stabilize the broken bone while the patient is transported to the hospital for more advanced treatment.
There are three main types of splints:
- Anatomical- In it, the non-injured body part is used to immobilize the injured body part. It is usually reserved for fingers and toes, but legs may also be splinted together in an emergency.
- Soft Splints: These involve using towels, cloths, blankets, or pillows to wrap around and immobilize the body part. This splint works very well with hand, ankle, or foot injuries.
- Rigid Splints: It refers to using a firm object such as cardboard, a piece of wood, a metal strip, folded newspaper, or other rigid items to immobilize the injured limb.
You should ensure that the splints are long enough so that they can immobilize the joint above and below the suspected fractured bone. Moreover, you should gather whatever splinting material is available before beginning the first aid for fractures. People should minimally try to realign bones and check for colour, warmth, and sensation. You should splint the injury in a position that is comfortable for the patient.
Control Any Bleeding
You should cover the wound with a sterile dressing or a clean cloth to avoid further contamination if it is an open fracture. To control the bleeding, you should also apply pressure around the injury and not over the bone coming out. Then secure the dressing with a bandage. A person should not try to push the bone or realign it. You should not use a tourniquet.
What Can I Do to Prevent Fractures?
- Follow a healthy diet with calcium and vitamin D to promote bone strength.
- Do weight-bearing exercises, as these help in keeping bones strong.
- Avoid using any form of tobacco, as tobacco and nicotine increase the risk of fractures of the bone.
- Osteoporosis is a major cause of fractures in the elderly. Talk to your medical practitioner about the risks associated with osteoporosis and get treatment if you suffer from it.
What Should I Not Do?
- You should not move the person unless the fractured bone is stable.
- You should not move a person with an injured spine, upper leg, hip, or pelvis unless absolutely necessary.
- You should not attempt to straighten the bone or change its position.
- You should not try to reposition a suspected spine injury.
- You should not test the fractured bone’s ability to move.
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider?
You should immediately seek medical assistance if you think you have a fractured bone, an open fracture, or an injury of the spine. You may also consult a doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Intense pain
- If you have a fractured body part that is turning blue or cold, it indicates loss of blood supply to the injured body part.
- The patient is not responding or is becoming unconscious.
- There is a suspected fractured bone in the neck, hip, head, pelvis, back, or upper leg.
- There is severe bleeding.
- You cannot immobilize the injury.
- A bone protrudes through the skin, or a limb or joint appears deformed.
- Even gentle pressure or movement causes pain.
Even though a sprain or strain may not be a medical emergency, they still deserve immediate medical attention to prevent further injury and deterioration. So, contact your medical practitioner if you have a sprain, strain, dislocation, or fractured bone.
Wrap Up:
Most people with fractured bones, sprains, or strains recover fully and return to their pre-injury routine. However, timely first-aid can help prevent further damage and speed up recovery. Paramedics play an important role in assessing potential injuries by looking for deformities, bruising, and swelling, providing first-aid to patients and preventing complications of bodily injuries. Hence, Tech Mahindra Foundation SMART Academies organized a webinar to impart information about First-aid techniques for broken bones, strains, and sprains. During the webinar, I familiarized the aspiring paramedics with the symptoms, causes, and first-aid procedures for fractured bones. The above blog contains the percepts of the information I shared during the webinar.

